Including vulnerable communities in extreme weather early warning systems
New technology can predict annual river floods with increasing accuracy, but the information is often inaccessible to the people who need it most. In this article, Rohini Pande and Maulik Jagnani describe an Inclusion Economics research collaboration with Google.org to identify what works in delivering flood warnings to people in India imperiled by rising waters.
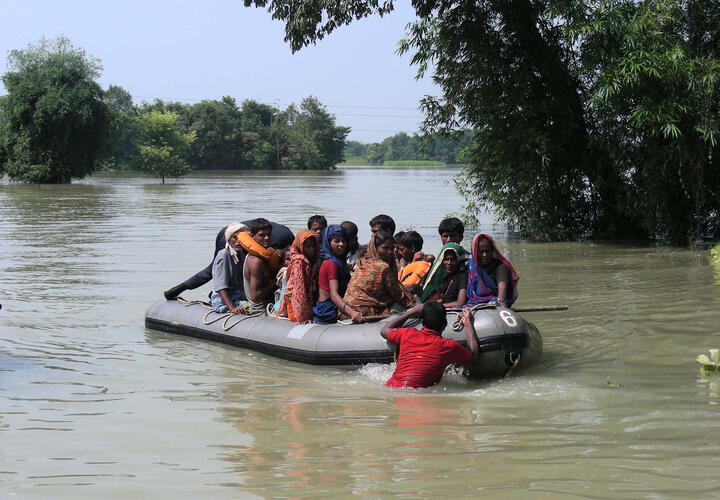

Jogender Yadav received no warning when his village in the Indian state of Bihar was flooded in 2022. “The river herself tells us when she is coming,” he said.
As river water inundated the village, fights broke out over the preservation of crops and livestock — the livelihood of the citizens. While his wife stayed on the rooftop of their home guarding their property, Jogender loaded his cattle onto a government-provided barge and headed to higher ground. When the waters receded a month later, their entire crop had been destroyed.
New technology can predict annual river floods with increasing accuracy. However, the information that predictive technology yields is often inaccessible to the people like Jogender who need it most. We are working with Google.org to identify what works in delivering flood warnings to the people in India most vulnerable by rising river waters, and have learned both technological and human innovation are necessary to protect the people most vulnerable to the impacts of flooding from the increasing effects of seasonal floods.
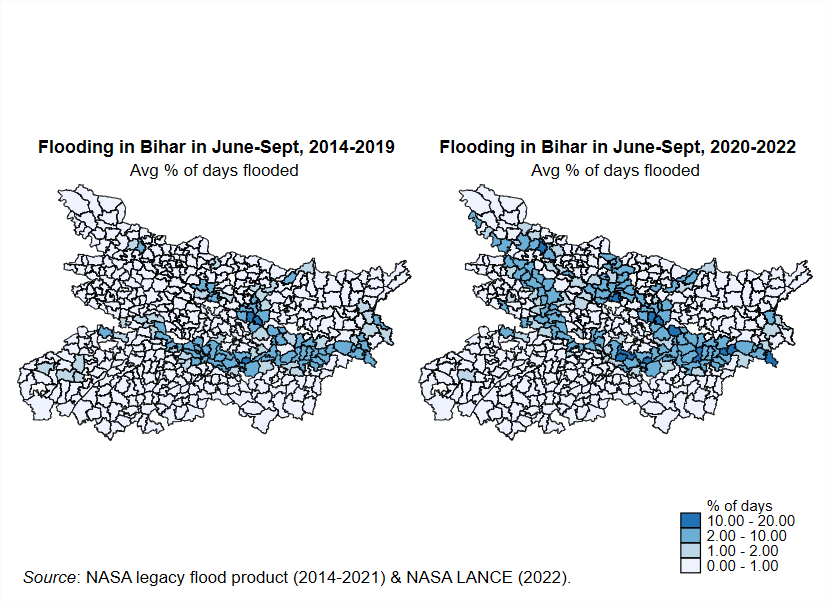
Riverine flood-detecting technologies are more valuable now than ever to communities in South Asia like the one where Jogender lives. South Asia is home to the world's largest population exposed to riverine flooding, and as India’s most flood-prone state, Bihar is under constant threat of flooding.
In surveys we conducted in the aftermath of the 2019 monsoon season in rural Bihar, 65% of the households reported a decrease in agricultural harvest and 31% of the households reported damage to their house as a result of floods. Similarly, 25% of the households reported losing at least one livestock during the months they faced floods.
Riverine floods are becoming more variable, both where they occur and when they occur. Jogender noted, “I’ve been seeing floods since I was born, but the villages nearby never used to get submerged.”
A large effort is underway to build global capacity for early flood warnings. Following on a 2022 UN report showing that only half of the countries in the world are covered by multi-hazard early warning systems, UN Secretary-General António Guterres announced that the UN would launch a $3.1 billion dollar “Early Warnings for All” initiative to fill the gaps.
However, general initiatives like this are not enough to protect individuals against riverine floods — which can be abrupt and hyperlocal in their effects. This necessitates a more “surgical” alerting protocol which encourages quick private protective actions.
Furthermore, the increasing variability of riverine floods makes them more difficult to avoid based on community knowledge and historical records, creating great potential for damage in communities that are not used to responding to severe flooding. To this point, Bihar has lacked both technical and logistical capacity to give effective early warnings and help people relocate.
Addressing these concerns, Google.org has created a machine learning forecasting system that can predict river floods: Daily satellite imagery of actual flooding from NASA confirms that Google alerts we sent were accurate harbingers of flooding. We have gone through years of trial-and-error with Google to effectively disseminate information to enable vulnerable individuals like Jogender to get the warnings they need to respond to flooding dangers.
Normally, small communities like those in Bihar have difficulties receiving warnings in time because of a range of challenges related to communication infrastructure and technology, state capacity and political context, and other social factors such as literacy levels and social trust. As a result, we now have built an early warning system for riverine floods that overcomes these last-mile challenges. The system pairs Google’s cutting-edge forecasting and android-based alerting system with monetarily incentivized grassroots volunteers trained in community outreach activities. This has the potential to prevent significant damage by ensuring that populations know when they are about to be exposed to significant flooding risk and have the time to prepare themselves and their communities.
As of now, we have deployed the system across 319 Bihari communities with over 3.6 million citizens. Initial results show that treatment communities were 27% more likely to receive any alerts between June and October 2022; received 2.37 more alerts (a 290% increase); 50% more likely to receive alerts before water reached their area; and also 57% more likely to report receiving highly accurate flood alerts.

An aerial view of a Bihar village during a 2008 river flood. Photos courtesy of Ministry of Defence (GODL-India), Wikimedia Commons.
These study results prove the new system’s high potential for saving lives and property. However, there are still remaining questions that we aim to investigate over the next few months: What is the final impact of this intervention? Are fewer assets lost and more lives saved as a result of this new early warning system?
Improvements in forecasting and harnessing the power of new technologies are an important investment to save lives, but their success is dependent on accessibility to vulnerable households. Pairing high-tech forecasting systems with low-tech community-based dissemination systems and building communities in this information is key to enabling protection from climate-related losses.
Ultimately, this research may hold lessons for the global development community, which is increasingly recognizing the importance of “last-mile” issues. Welfare-improving technologies – from improved fertilizers to vaccines – often falter at the point where they must reach the individual to have an effect. This is often because the low-income people who need them tend to live in rural areas, isolated from infrastructure and communication networks. Our work suggests that engaging community intermediaries may be a good way to go the last mile and make a difference.
The authors wish to thank Sathia Chakrapani, Advait Moharir , Surya R, and Rajesh Sarma for conducting interviews; Satish Wasti for analysis; and Jenna Allard, Vestal McIntyre and Noah Robinson for editorial assistance on this article.